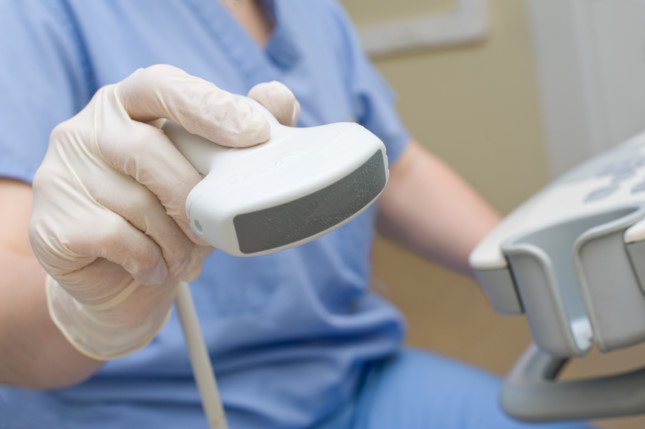
The chest wall echocardiogram is the most common echocardiography technique. During a thoracic wall ultrasound, a probe is placed along the left or right bank of the sternum, the heart tip, the pectoral (to see the aortic valve, left ventricular output and descending aorta), or the lower position. sadness. Ultrasound of the chest wall provides 2 or 3-dimensional images of most of the major heart structures. A preliminary echocardiogram is sometimes performed in bed on critically ill patients in the intensive care unit or emergency department (to assess pericardial fluid and left ventricular function). Resuscitation doctors or emergency physicians are often trained to do preliminary echocardiography because cardiologists are not always available in these units. A preliminary echocardiogram through the thoracic wall can be performed with a portable ultrasound to detect pericardial fluid, assess heart valve function and ventricular function. Portable ultrasound is very useful for preliminary screening, thereby knowing which patients need a more detailed echocardiogram.
In transesophageal echocardiography, a probe on the end of the endoscope allows the heart to be viewed from the stomach and esophagus. Transesophageal echocardiography is used to diagnose when trans-thoracic echocardiography is difficult, for example in obese patients and in COPD patients. Transesophageal echocardiography provides a clearer picture of small abnormal structures (for example, endocardial warts or oval holes). It also allows us to easily observe the posterior structures near the esophageal tube such as the left atrium, the left atrium, the interrrial septum, pulmonary vein anatomy. Transesophageal echocardiography may also provide imaging of the ascending aorta, images of structures <3 mm (eg thrombosis, warts), and artificial valves.
During an ultrasound in the heart chamber, a probe mounted at the end of the catheter (inserted through the thigh vein into the heart) allows the anatomical structure of the heart to be viewed. Echocardiography can be used during complex cardiovascular interventions (for example, closing the atrial ventricular or percutaneous oval) or during electrophysiological exploration of the heart. Ultrasound in the chambers of the heart provides better image quality and reduces the duration of the procedure when compared with transesophageal ultrasound. However, an ultrasound in the heart chamber is generally more expensive.
Methodology
Two-plane ultrasound is the most widely used. Ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound help provide more information. Three-dimensional ultrasound is especially useful in evaluating the mitral valve apparatus to guide surgery.
A contrast echocardiogram is a 2-sided ultrasound performed during a rapid injection of a saline solution (or another contrast agent into the circulatory system.) This effervescent saline solution when injected. The vein returns to the right heart chamber, then, if there is an opening in the heart wall, the foam will be seen in the left heart chamber.Usually, the diaphragm does not pass through the pulmonary capillary system. an albumin-type sound-blocking foam can travel through the pulmonary system to the heart and thereby help us see the heart's structure, especially the left ventricle.
Doppler ultrasound helps you determine the speed, direction, and type of blood flow. This technique is very useful for detecting abnormal blood flow (eg in a heart valve) or abnormal velocity of blood flow (eg in heart valve stenosis). Doppler ultrasound does not provide spatial information such as the size and shape of the heart and its structures.
Color Doppler ultrasound combines 2-plane echocardiography and Doppler ultrasound to provide information about the size and shape of the heart and its structures as well as the velocity and direction of blood flow through the valves and its outlet routes. ventricle. Color spectrum in ultrasound is used to encode blood flow. By convention, red indicates blood flow toward the transducer, blue indicates blood flow away from the transducer.
Tissue Doppler ultrasound uses the Doppler technique to measure the contractile velocity of the heart muscle (rather than blood flow). These data can be used to calculate myocardial contractility (percentage change of measure between myocardial contraction and myocardial dilation) and rate of myocardial contraction (rate of change of measure). . The force of contraction and the rate of myocardial contraction can help assess systolic and diastolic function and determine myocardial ischemia during exercise exercise.
The triaxial echocardiogram combines M-mode ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound, and tissue Doppler ultrasound to create a real-time hologram of cardiac anatomy and function. This technique is still being researched and developed, but its widespread application is limited due to cost issues.









 A12 - 55 - 57 Lê Trọng Tấn, Khu phố Bình Đường 2, Phường An Bình, TP. Dĩ An, Bình Dương
A12 - 55 - 57 Lê Trọng Tấn, Khu phố Bình Đường 2, Phường An Bình, TP. Dĩ An, Bình Dương Điện thoại: 0274.3792 803 - 0274.3790 106 - Số hotline: 0943 508 778
Điện thoại: 0274.3792 803 - 0274.3790 106 - Số hotline: 0943 508 778 medicdian@gmail.com
medicdian@gmail.com www.medicdian.com
www.medicdian.com
