The early years of life are especially important for a child's development. Therefore, doctors must be very careful in prescribing drugs for children, especially antibiotics. Antibiotics can cause problems such as antibiotic resistance, diarrhea and especially drug allergies. So what to do when a baby has an antibiotic allergy?
1. What is an antibiotic?
To know what to do when your baby has an antibiotic allergy, you need to know what antibiotics are.
Antibiotics are drugs used to fight infections caused by bacteria. The drug helps to fight when the number of harmful bacteria is too much, the immune system cannot control it. Its anti-bacterial mechanism is to kill bacteria or slow or stop the growth of bacteria.
The first antibiotic was penicillin. Before antibiotics, 30% of all deaths were caused by bacterial infections. Currently, there are many different groups of antibiotics. Some antibiotics work best for a specific type of bacterial infection. There are broad-spectrum and narrow-spectrum antibiotics; There are antibiotics that attack aerobic bacteria and attack anaerobic bacteria.
In most countries, antibiotics are prescription drugs with the exception of some antibiotic creams and ointments. Antibiotics come in many forms:

2. What are the effects of antibiotics on a child?
The early years of life are especially important for a child's development, and the use of antibiotics should be considered by a doctor. If the illness is mild, your doctor may recommend non-antibiotic monitoring or treatment. But there are cases where antibiotics are an effective treatment for young children.
Most of the common cold symptoms such as runny nose, cough and stuffy nose, sore throat, fever and ear infections are caused by viruses, and should not be treated with antibiotics. However, sometimes serious diseases such as pneumonia, pertussis, urinary tract infections, bacterial sinusitis or streptococcal pharyngitis, severe and recurrent ear infections ... also have the above symptoms. is caused by bacteria. Therefore, these diseases can be effectively treated with antibiotics. In addition, some children with more difficult to heal conditions such as cleft palate surgery, immune disorders, cochlear implantation, can prescribe antibiotics.
Inappropriate use of antibiotics can cause antibiotic resistance. In addition, antibiotics can kill good bacteria that cause diarrhea or cause bad bacteria to multiply quickly and cause infections that are difficult to control. In particular, the drug can cause an allergy to antibiotics.
3. What to do when a child has an allergy to antibiotics?
One out of every 10 children takes antibiotics. Be sure to tell your doctor about an allergy history if your baby has previous antibiotic allergy.
3.1. Symptoms of an allergy to antibiotics
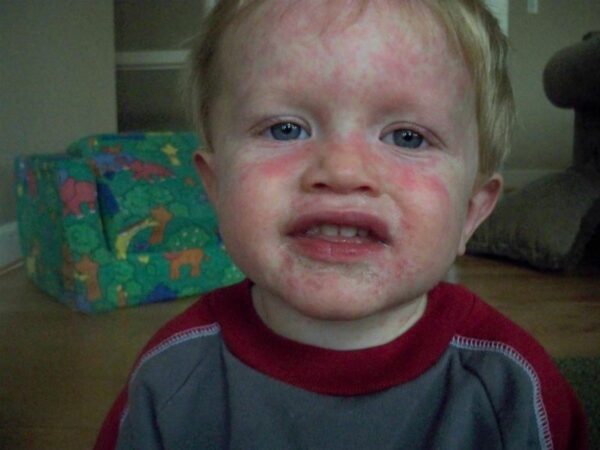
Allergy to penicillins is the most common drug allergy. Drug allergies can cause life-threatening reactions, but fortunately most babies with antibiotic allergies experience only milder ones.
Common symptoms are itchiness, hives (such as hives), difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face, hands or feet. Less common are vomiting, diarrhea or lightheadedness. Usually two or more of these symptoms appear in an allergic reaction and usually start within two hours of taking the medicine.
Babies with an antibiotic allergy with severe symptoms will have a similar skin rash, such as erythema multiforme with wheezing, difficulty breathing, difficulty swallowing, or swelling of the mouth or throat; as well as anaphylaxis - a severe allergic reaction.
3.2. Treatment
You can contact your doctor, sometimes allergy tests and questionnaires can determine if your baby has an allergy to antibiotics.
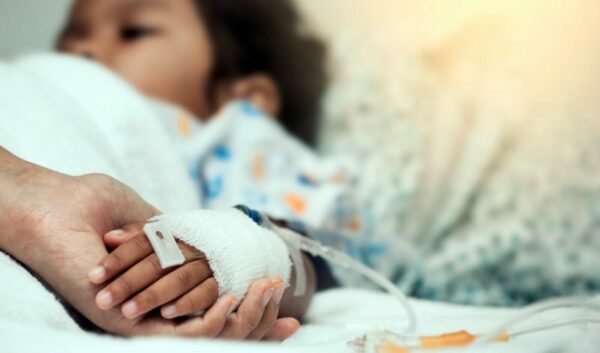
3.2.1. First aid and urgent care
Because anaphylaxis can be life-threatening, you need to recognize the symptoms and how to handle a medical emergency. Blistering, swelling, and wheezing are common symptoms.
- Stop allergy medication immediately.
- Call ambulance.
- If you have an epinephrine syringe, use it at the first sign of symptoms. One injection may not be enough to stop anaphylaxis. A repeat dose may be required after 5 - 10 minutes if severe symptoms persist.
- While waiting for emergency care when your baby has an allergy to antibiotics:
- Take the child to the emergency hospital as quickly as possible for evaluation depending on the history, health and clinical progress. It is very important to follow the hospital for a few hours because anaphylaxis can return.
3.2.2. Medicine treatment
Children with an antibiotic allergy may be prescribed treatment with:
If your child is at high risk or has ever had anaphylaxis, you should always have epinephrine ready. Children old enough will be taught by health professionals how to self-administer epinephrine when needed. The drug is packed in 1 standard dose in the auto-injector (EpiPen or Auvi-Q).
4. Prevent antibiotic allergy in children
To prevent antibiotic allergy in a child, you need to keep in mind:
After an episode of anaphylaxis, you may be referred to an allergist to:
Antibiotics help treat bacterial infections. However, the drug can cause a drug allergy, which can be life-threatening. The early years of life are very important for children. When your baby is sick, take your baby to the doctor for effective prescription and reasonable dose adjustment!















 99/6 Nơ Trang Long, Phường 14, Bình Thạnh, Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh, Vietnam
99/6 Nơ Trang Long, Phường 14, Bình Thạnh, Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh, Vietnam
 0914 999 999
0914 999 999
 green.jsc@gmail.com
green.jsc@gmail.com
 www.greenpharma.com.vn
www.greenpharma.com.vn
Hotline
Hotline
