The seasonal weather makes people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease uncomfortable, tired, or even worse. Therefore, in the course of taking medicines, the patient needs to listen to his or her body and detect possible side effects and respond accordingly.
Bronchodilators
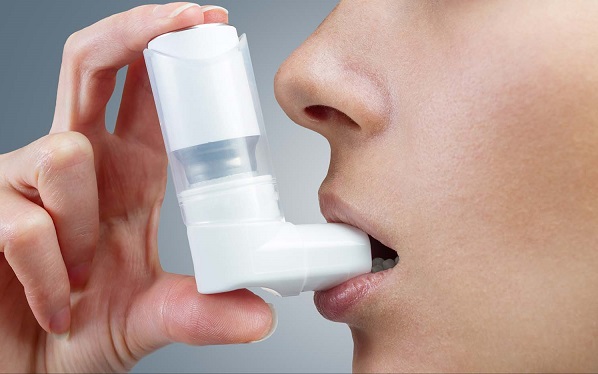
As the central group of drugs in the treatment of COPD, the drug changes the bronchial smooth muscle tone, thus increasing the airway diameter to help the patient breathe more easily. Bronchodilators are preferred in inhaled and nebulized forms because the dose is much lower than the systemic dose. Bronchodilators include reliever medications and maintenance medications. The main groups of bronchodilators:
Beta-2 booster drugs: Includes short acting drugs (salbutamol, terbutaline) with a reliever role and a long acting form (salmetarol, formoterol, indacaterol) for maintenance. The long-acting form is common in the treatment of COPD.
Side effects of beta-2 booster drugs patients who complain a lot are tremor and tachycardia, palpitations, palpitations. Most of the hand tremors are benign and mild, and when the drug is stopped, they will go away. Tachycardia appears with different degrees and depends on each patient. Other possible side effects: irritability, insomnia, nausea, weakness, dizziness ... Most of these symptoms are only transient and rarely have to stop treatment because of these side effects. .
Caution should be exercised when using this drug in patients with hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, especially tachycardia, ischemic heart disease. Therefore, patients need to inform their doctors about co-morbid diseases so that they can choose the right drugs and can consult a specialist on supplementing drugs to reduce side effects when using drugs. necessary.
Anticholinergic group: This group also has two types of short acting (ipratropium) and long acting form (tiotropium). Common side effects are similar to those of beta-2 boosters: tremor, tachycardia. Like the beta-2 group, these effects are usually mild.
In addition, side effects may be encountered when using this group of drugs: In the eyes such as dilated pupils, increased intraocular pressure, narrow angle glaucoma, eye pain. If the patient experiences these side effects, it is necessary to immediately see an eye specialist for timely treatment. In the gastrointestinal tract, the drug can cause dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation ... To overcome, the patient can drink more water when dry mouth, adjust the reasonable diet and the doctor can use adjuvant medicine. In the urinary tract, the drug can cause urinary retention, so be careful in patients with obstructive urinary tract such as prostate enlargement that can cause acute urinary retention.
The two groups of bronchodilators on systemic administration had more side effects. The lower dose inhaled bronchodilators, the reduced and acceptable side effects. The long-acting inhalation form is preferred because of its higher efficiency and comfort for the patient. The form of a combination of the two above bronchodilators increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces the rate of side effects when using a bronchodilator alone.
In addition, another group of bronchodilators but rarely used is the xanthin group, which consists mainly of the oral drug form (theophylin) and the intravenous form (diaphylin). Side effects of this group: nausea, epigastric pain, diarrhea, tremor, tachycardia ... Due to the close therapeutic dose and toxic dose, it is rarely used in combination with other bronchodilators. Absolutely not using the drug without a doctor's prescription is very dangerous.
The seasonal weather makes people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease uncomfortable, tired, or even worse. Therefore, in the course of taking medicines, the patient needs to listen to his or her body and detect possible side effects and respond accordingly.
Bronchodilators
As the central group of drugs in the treatment of COPD, the drug changes the bronchial smooth muscle tone, thus increasing the airway diameter to help the patient breathe more easily. Bronchodilators are preferred in inhaled and nebulized forms because the dose is much lower than the systemic dose. Bronchodilators include reliever medications and maintenance medications. The main groups of bronchodilators:
Beta-2 booster drugs: Includes short acting drugs (salbutamol, terbutaline) with a reliever role and a long acting form (salmetarol, formoterol, indacaterol) for maintenance. The long-acting form is common in the treatment of COPD.
Side effects of beta-2 booster drugs patients who complain a lot are tremor and tachycardia, palpitations, palpitations. Most of the hand tremors are benign and mild, and when the drug is stopped, they will go away. Tachycardia appears with different degrees and depends on each patient. Other possible side effects: irritability, insomnia, nausea, weakness, dizziness ... Most of these symptoms are only transient and rarely have to stop treatment because of these side effects. .
Caution should be exercised when using this drug in patients with hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, especially tachycardia, ischemic heart disease. Therefore, patients need to inform their doctors about co-morbid diseases so that they can choose the right drugs and can consult a specialist on supplementing drugs to reduce side effects when using drugs. necessary.
Anticholinergic group: This group also has two types of short acting (ipratropium) and long acting form (tiotropium). Common side effects are similar to those of beta-2 boosters: tremor, tachycardia. Like the beta-2 group, these effects are usually mild.
In addition, side effects may be encountered when using this group of drugs: In the eyes such as dilated pupils, increased intraocular pressure, narrow angle glaucoma, eye pain. If the patient experiences these side effects, it is necessary to immediately see an eye specialist for timely treatment. In the gastrointestinal tract, the drug can cause dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation ... To overcome, the patient can drink more water when dry mouth, adjust the reasonable diet and the doctor can use adjuvant medicine. In the urinary tract, the drug can cause urinary retention, so be careful in patients with obstructive urinary tract such as prostate enlargement that can cause acute urinary retention.
The two groups of bronchodilators on systemic administration had more side effects. The lower dose inhaled bronchodilators, the reduced and acceptable side effects. The long-acting inhalation form is preferred because of its higher efficiency and comfort for the patient. The form of a combination of the two above bronchodilators increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces the rate of side effects when using a bronchodilator alone.
In addition, another group of bronchodilators but rarely used is the xanthin group, which consists mainly of the oral drug form (theophylin) and the intravenous form (diaphylin). Side effects of this group: nausea, epigastric pain, diarrhea, tremor, tachycardia ... Due to the close therapeutic dose and toxic dose, it is rarely used in combination with other bronchodilators. Absolutely not using the drug without a doctor's prescription is very dangerous.
Corticosteroids
This class includes injectable, oral and inhaled form. Systemic corticosteroids should be used for short-term only during an exacerbation to help significantly improve respiratory function. Prolonged use of corticosteroids causes many side effects on the digestive system such as peptic ulcers, even gastrointestinal bleeding ...; for the nervous system: paranoia, depression ...; increased risk of infection; on the skin: thin skin, stretch marks, dense hair, acne; for bones: osteoporosis; In the eyes: Cataracts; hypertension, metabolic disorders ...
To reduce side effects of corticosteroids, you need to comply with the prescription of your doctor, do not arbitrarily buy drugs for use, use inhaled corticosteroids with long-acting beta-2 enhancement drugs to increase efficiency and reduce dosage of the drug, thereby reducing side effects. During treatment, the doctor adjusts the dose, screen for side effects and supplements the medication and advises a diet and exercise regimen to maximize control of side effects. Adherence to treatment will help slow the natural course of the disease, improve quality of life and prolong life.
According to suckhoedoisong










 A12 - 55 - 57 Lê Trọng Tấn, Khu phố Bình Đường 2, Phường An Bình, TP. Dĩ An, Bình Dương
A12 - 55 - 57 Lê Trọng Tấn, Khu phố Bình Đường 2, Phường An Bình, TP. Dĩ An, Bình Dương Điện thoại: 0274.3792 803 - 0274.3790 106 - Số hotline: 0943 508 778
Điện thoại: 0274.3792 803 - 0274.3790 106 - Số hotline: 0943 508 778 medicdian@gmail.com
medicdian@gmail.com www.medicdian.com
www.medicdian.com
